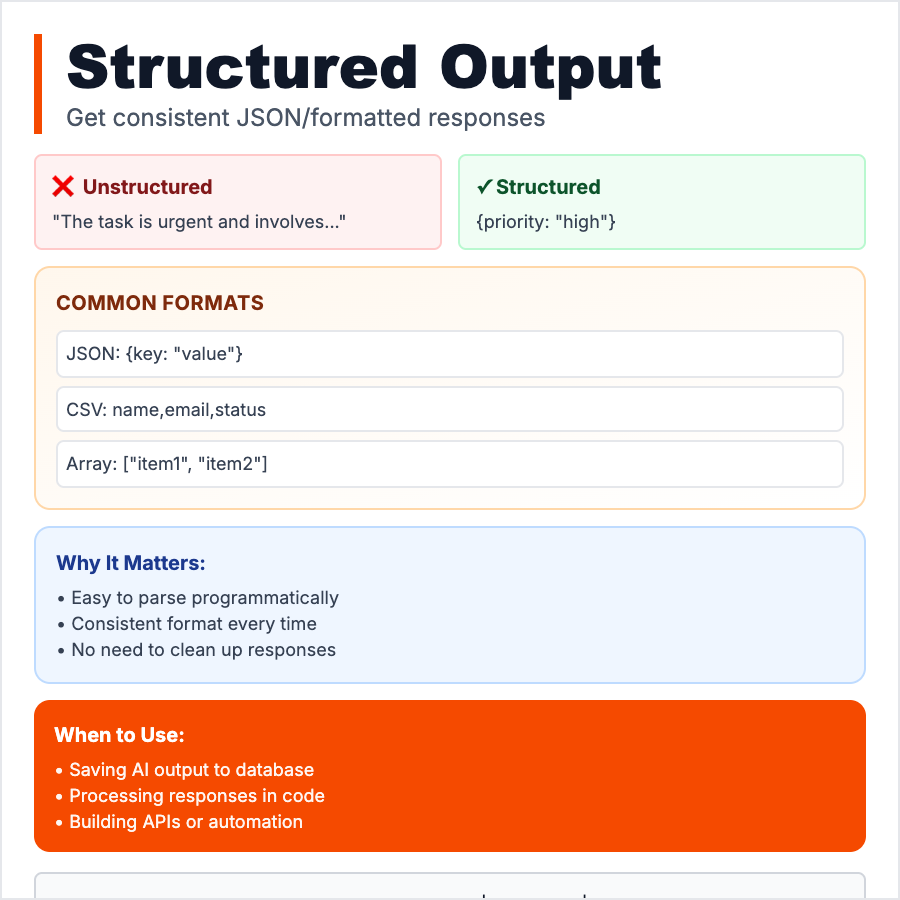
What is Structured Output?
Structured Output is when you force the AI to return data in a specific, machine-readable format (JSON, XML, CSV, YAML) instead of freeform text. You define a schema (e.g., "return {name, email, score}") and the AI fills it in. This makes AI outputs predictable, parsable, and easy to integrate into apps, databases, or workflows—no more regex-parsing messy text.
When Should You Use This?
Use structured output when integrating AI into software systems where you need predictable, parsable data. Examples: extracting data from text (invoices, resumes, forms), generating configs/settings, building AI-powered APIs, populating databases, creating data pipelines. OpenAI's "JSON Mode" and function calling enforce this. Always provide a clear schema/example in your prompt.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- •Not enforcing the format—AI may ignore your request; use JSON Mode or validate outputs
- •Complex schemas without examples—show the AI exactly what you want with a sample output
- •Forgetting to handle failures—AI can still return invalid JSON; parse + validate on your end
- •Over-constraining—too many nested fields or strict rules make AI fail; start simple
- •Not testing edge cases—AI may invent fields, skip required ones, or format incorrectly
Real-World Examples
- •OpenAI JSON Mode—set response_format: "json_object" to guarantee valid JSON output
- •Zapier—uses structured output to extract form data from emails and populate Google Sheets
- •Invoice parsing—AI extracts {vendor, amount, date, items[]} from PDF invoices
- •Resume screening—AI returns {name, email, skills[], experience[], education[]} for easy filtering
Category
Ai Vocabulary