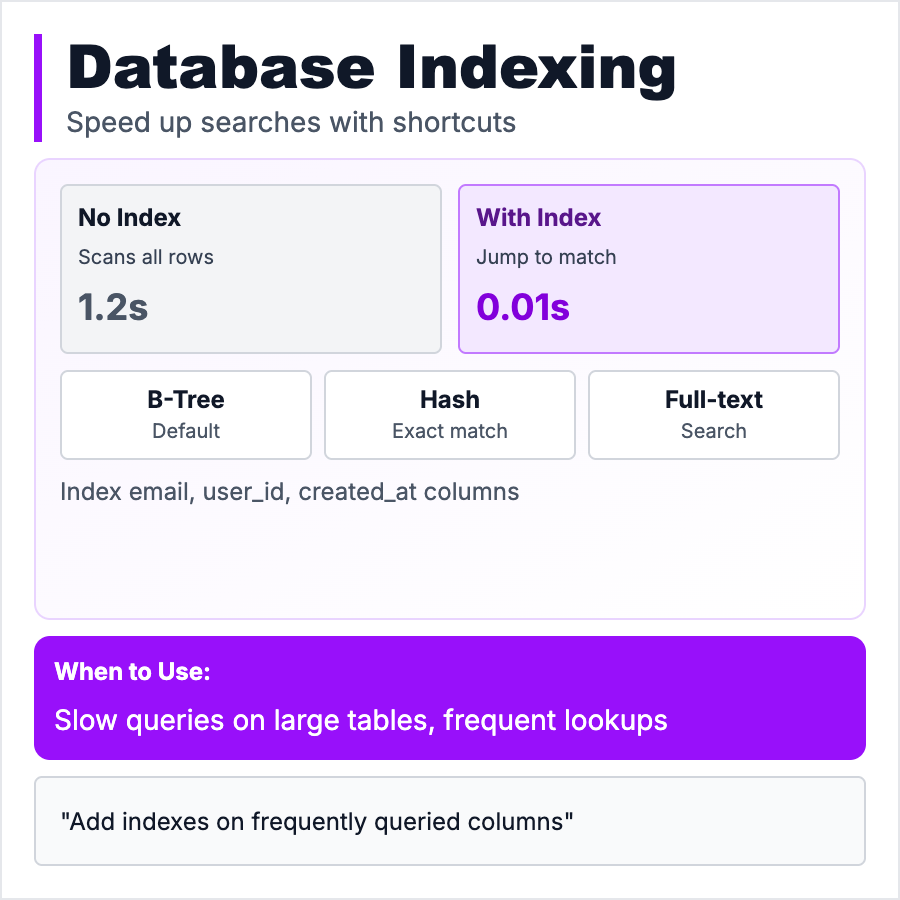
What is Database Indexing?
Database Indexing creates a lookup table to make queries fast. Like a book index—instead of reading every page to find "Napoleon," check the index. Query without index: scan 1M rows (slow). Query with index: jump directly to result (fast). Indexes speed up reads but slow down writes (index must be updated). Most important database optimization. Add indexes on columns you query frequently (WHERE, JOIN, ORDER BY).
When Should You Use This?
Add indexes when queries are slow (check EXPLAIN output), on foreign keys (JOIN columns), on columns in WHERE clauses, or on frequently sorted/filtered columns. Start with primary key (auto-indexed). Don't index everything—each index slows writes and uses disk space. Index strategically based on actual query patterns. Use database query analyzer to find slow queries, then add indexes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- •No indexes—scanning full table for every query
- •Too many indexes—every insert updates 10 indexes, writes become slow
- •Wrong columns—indexing rarely-queried columns wastes space
- •Ignoring composite indexes—(user_id, created_at) index faster than two separate indexes
- •Not monitoring—index helps initially, becomes useless as data changes
Real-World Examples
- •E-commerce—Index on product.category for fast category pages
- •Social media—Index on posts.user_id and posts.created_at for user timelines
- •SaaS—Index on users.email for fast login lookups
- •Analytics—Composite index on (user_id, event_type, timestamp) for dashboards
Category
System Design Patterns